Managing money is a big job for businesses. A good financial manager can make this easier. This post will show how they help keep a company's finances healthy and strong. Keep reading to learn more!
What is a Financial Manager?
A financial manager plays a crucial role in any organization. They take care of the company's finances, making sure that it stays healthy and grows. This includes managing cash flow, preparing financial statements, and keeping an eye on the market to guide investment decisions.
They work closely with senior managers to plan for the future and make smart choices that boost the company's financial stability.
Financial managers are key players in helping businesses maximize profitability and ensure long-term growth.
Their job involves analyzing data to produce reports on how well the business is doing financially. They also develop budgets to control spending and increase profits. Alongside this, they monitor how money moves in and out of the business daily.
It’s their responsibility to comply with laws on handling finances, advising companies on investments, risk management, and planning for economic ups and downs.
Key Roles and Responsibilities of a Financial Manager
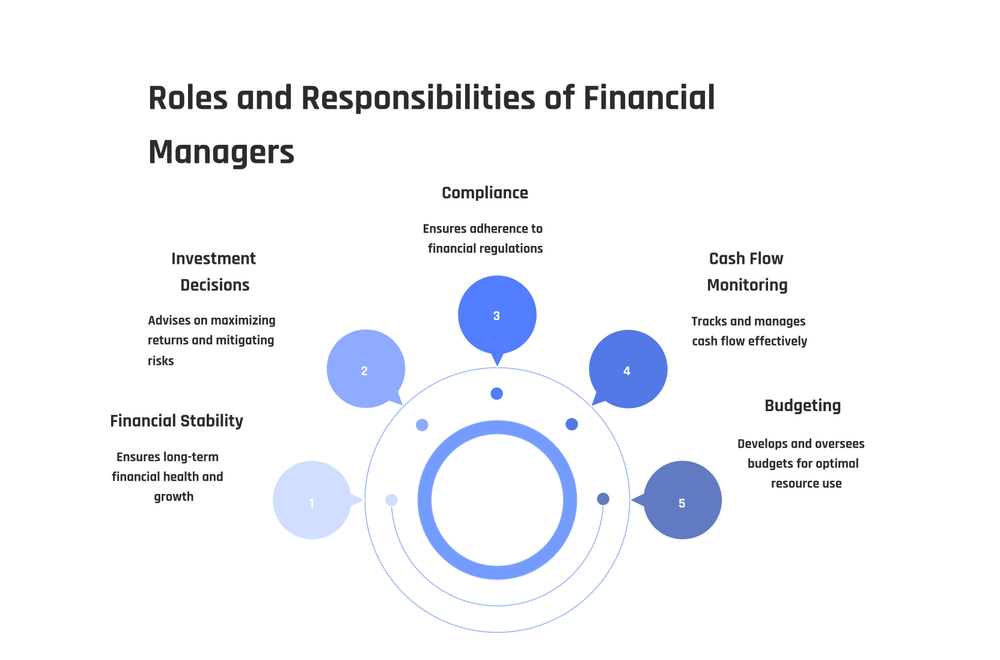
Financial managers prepare and analyze financial reports. They develop and oversee budgets, monitor cash flow, ensure compliance with financial regulations, and advise on investment decisions.
Preparing and analyzing financial reports
Preparing and analyzing financial reports is a key job for financial managers. They take care of all the numbers related to a company's money matters. These reports help them understand how well the business is doing.
Financial managers look at sales, costs, and profits to make sure everything adds up right. They also check if the company can pay its bills on time and plan for future expenses.
They use these reports to suggest ways to improve financial health. This might involve finding areas where the company can spend less or make more money. Analysis of financial data helps in making smart decisions about where to invest funds too.
Developing and overseeing budgets
Financial managers play a crucial role in shaping and managing budgets. Their primary responsibility is to ensure optimal utilization of the company's finances to achieve its objectives.
This includes identifying the financial needs of different business segments, such as new initiatives or routine operations. Collaborating closely with other departments, financial managers establish and monitor budgets with precision.
By doing so, they prevent excessive expenditure and ensure the availability of funds for vital operations.
They also respond to financial conditions of the company by amending budgets as required. If a section incurs excessive costs, financial managers strategize the resolution without affecting the company's collective performance.
Subsequently, their attention shifts to monitoring cash flow and maintaining a watchful eye on the organization's financial status.
Efficient budgeting supports companies through financial obstacles by distributing resources judiciously.
Monitoring cash flow and financial health
Financial managers play a crucial role in monitoring the cash flow and financial health of an organization. They track the movement of money in and out of the company to ensure that there is enough cash to cover expenses and invest in growth opportunities.
By analyzing financial reports, they can pinpoint any areas of concern and take necessary actions to maintain a healthy cash flow. Financial managers also keep a keen eye on the overall financial health of the company, which involves assessing its profitability, liquidity, and solvency.
This vigilance helps them make informed decisions regarding investments, managing risks, and ensuring the long-term financial stability of the organization.
Ensuring compliance with financial regulations
Financial managers play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with financial regulations to avoid legal and financial consequences for their organizations. This involves staying updated with tax laws, market regulations, and industry standards to make sure the company's financial activities align with all requirements.
They need to monitor changes in government policies that may impact the organization's finances, making adjustments as necessary to ensure adherence to new rules and regulations. In addition, they work closely with legal and compliance teams within the organization to guarantee that all financial practices abide by relevant laws and guidelines while mitigating potential risks associated with non-compliance.
Given the complexities of evolving regulatory frameworks, finance managers must maintain precise attention towards fulfilling legal requirements regarding credit limits, implementing strategies crafted for business continuity plans, managing operational expenses supporting sustainable growth goals while minimizing risks related to market fluctuations or interest rates.
Advising on investment decisions
After ensuring compliance with financial regulations, financial managers play a pivotal role in advising on investment decisions. This involves evaluating potential investment opportunities and recommending strategies to maximize returns while mitigating risks.
Financial managers rely on their expertise in areas such as risk management and strategic planning to guide organizations towards sound investment choices. They utilize their proficiency in financial analysis to assess market trends and identify lucrative prospects for growing the company's assets.
In addition, they provide insights into portfolio management, assisting businesses in allocating resources effectively to attain profit-maximizing outcomes.
Financial managers need to navigate market conditions carefully, supporting effective financial management goals with comprehensive data analysis and a deep understanding of industry trends.
Their ability to implement customized strategies towards managing investments ensures that organizations make informed decisions in a constantly changing financial future.
Core Skills Required for Financial Managers

Financial managers need to excel in financial analysis and forecasting, as well as strategic planning and decision-making. They are also required to possess strong risk assessment and management abilities, along with effective communication and leadership skills.
Financial analysis and forecasting
Financial analysis plays a crucial role for financial managers as it entails examining a company's financial performance using techniques like ratio analysis and cash flow analysis.
This aids in evaluating the company's profitability, efficiency, and liquidity. Forecasting, conversely, entails predicting future financial trends based on historical data and market conditions.
Financial managers utilize these forecasts to make well-informed decisions regarding investments, budgets, and overall financial planning.
Furthermore, through conducting financial analysis and forecasting, financial managers can identify potential risks or opportunities for the company. Analyzing past trends can assist in projecting future scenarios accurately.
This enables sound strategic planning and decision-making to optimize the company's financial resources effectively. Also, it assists in evaluating investment options for maximizing profits while mitigating risks within regulatory compliance parameters.
Strategic planning and decision-making
After analyzing financial data and forecasting future trends, financial managers must engage in strategic planning and decision-making. This involves crafting long-term financial goals for the company and implementing strategies to achieve them.
This process also includes making important decisions regarding investments, capital budgeting, and determining the optimal capital structure for the organization. Financial managers constantly evaluate market risks while navigating through ever-evolving economic conditions.
They play a crucial role in steering the company towards success by making sound financial decisions that align with its overall business objectives.
The responsibility of strategic planning and decision-making is crucial as it directly impacts the company's financial health, profitability, and growth trajectory. Financial managers need to be adept at balancing risk while striving to enhance profitability through prudent decision-making.
Moreover, they are tasked with ensuring that their decisions comply with relevant regulations and contribute positively to the company's working capital management.
Risk assessment and management
Financial managers play a vital role in assessing and managing risks to ensure the financial health of their organization. They are responsible for identifying potential risks, analyzing their potential impact, and developing strategies to mitigate them.
This involves closely monitoring market fluctuations, regulatory changes, and operational risks to make informed decisions that balance risk and profitability. Additionally, financial managers utilize their expertise in risk management to implement customized strategies that support the company's financial stability while dealing with challenges such as credit risk, investment management, and cash flow.
Financial managers also significantly contribute to efficient risk assessment by implementing strong financial controls, conducting thorough financial ratio analysis, and creating comprehensive business activity reports.
These professionals engage in the constantly changing world of finance with detailed approaches aimed at mitigating risks in areas such as corporate finance, investment management, and government compliance.
With a median annual wage of $134,180 as reported by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics in 2020, these roles demand a thorough understanding not only of finance but also of strategic planning to effectively address challenges.
Communication and leadership skills
Financial managers need strong communication and leadership skills to effectively lead finance teams and communicate complex financial information. Essential for presenting financial reports, advising on investment decisions, and collaborating with other departments.
Crucial for guiding finance teams, implementing strategies, and mitigating risks. Moreover, financial managers must be able to convey financial data in a clear and understandable manner to stakeholders such as company executives or shareholders.
These skills help them take charge of challenging situations like market fluctuations and regulatory changes. Financial managers with strong communication abilities can clearly articulate the rationale behind their investment decisions or budget allocations, gaining trust from both internal and external stakeholders.
Strong leadership helps in steering finance teams through ever-evolving complexities in the realm of risk management or corporate finance while ensuring that everyone works towards the firm's overall goal of maintaining financial health.
Areas of Expertise for Financial Managers
Financial managers specialize in corporate finance, risk management, investment and portfolio management, and government and regulatory compliance. They bring expertise to navigate the intricacies of financial regulations and dynamic market conditions for optimum results.
Corporate finance
Financial managers specializing in corporate finance are responsible for overseeing a company's financial activities. They manage the company's investment strategies and financial performance, ensuring that the business is on track to meet its financial goals.
Corporate finance managers analyze data to make strategic decisions regarding investments, mergers, and acquisitions while also evaluating the company's capital structure and managing its cash flow.
Additionally, they play a crucial role in maximizing shareholder value by determining how best to allocate resources within the organization.
The ability of corporate finance managers to effectively manage risk is essential. They must be adept at assessing potential risks associated with different investments or projects and develop strategies to mitigate these risks.
Moreover, their expertise in areas such as financial analysis and forecasting equips them with the skills needed to inform critical decisions that impact a company’s overall financial health.
Risk management
Financial managers play a crucial role in risk management, ensuring that the organization identifies and mitigates potential financial risks. They oversee strategies to minimize exposure to uncertain or adverse events that could impact the company's financial health.
This includes analyzing market trends, assessing investment risks, and implementing measures to safeguard the company's assets and investments. With their expertise in risk assessment and management, financial managers strive to create strong frameworks that protect the organization from potential financial challenges while maximizing profitability.
Financial managers must navigate an ever-changing financial landscape armed with skills like risk analysis, credit evaluation, and strategic planning. They are responsible for anticipating potential threats to the organization's finances through careful risk assessments while implementing customized risk management strategies aimed at protecting against unforeseen challenges in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Investment and portfolio management
Financial managers specializing in investment and portfolio management are responsible for overseeing the organization's investment strategies. They analyze market trends, assess risk, and make decisions about where to invest the company's money.
This role requires a keen understanding of financial markets and various investment vehicles such as mutual funds, stocks, and bonds. The goal is to maximize returns while managing risks effectively.
Strong analytical skills coupled with an in-depth knowledge of different investment options are crucial for success in this area.
In this area, precision is key as these professionals need to stay updated on constantly changing market dynamics to ensure that investments align with organizational objectives and meet desired outcomes.
Accordingly, they work closely with financial analysts to gather data insights that support their strategic decisions. Not only do they manage current investments with great care; they also design customized strategies for future growth opportunities within the market—ultimately contributing significantly towards the company’s overall financial health.
Government and regulatory compliance
Financial managers play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with government regulations. They stay updated on financial laws and guidelines to protect their organizations from legal issues.
This involves carefully reviewing, interpreting, and implementing financial regulations to ensure all activities adhere to the set standards. Failure to comply could lead to hefty fines or legal action, emphasizing the importance of this aspect of their job.
Moreover, they work closely with internal and external auditors to guarantee adherence while devising strategies that align with these regulatory requirements.
The implementation of government and regulatory compliance involves dealing with complex rules like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) and Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act.
Financial managers also need to consider industry-specific regulations such as those set by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) for financial institutions or healthcare compliances for insurance companies.
How to Become a Financial Manager
To become a financial manager, acquire the necessary education, gain relevant work experience, and pursue certifications like CFA or CPA. For more on this topic, read our blog!
Education requirements
Financial managers typically need at least a bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, economics, or business administration. Some employers may prefer candidates with a master's degree for advanced roles.
Courses in financial analysis, risk management, and investments are crucial to develop the necessary expertise. Moreover, aspiring financial managers can pursue certifications such as Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) or Certified Public Accountant (CPA) to enhance their credentials and stand out in the competitive job market.
In addition, gaining relevant work experience is essential for aspiring financial managers. This often involves starting in entry-level positions like financial analysts or accountants before advancing to managerial roles.
Acquiring hands-on experience provides a deeper understanding of financial operations and the practical application of theoretical knowledge. Furthermore, building strong analytical and leadership skills during these formative years is vital for success as a financial manager later on.
Gaining relevant work experience
After meeting the education requirements, gaining relevant work experience is crucial for aspiring financial managers. This could involve internships or entry-level roles in finance and accounting departments.
While working, individuals should focus on preparing financial statements, managing investments, and developing cash management skills. They can also seek out positions in credit or insurance management to learn about risk assessment and mitigation strategies firsthand.
Acquiring hands-on experience will not just hone their analytical and detail-oriented abilities but also build a strong foundation for future leadership roles in financial management as they navigate real-world complexities within the ever-evolving realm of finance.
It's an opportunity to implement the strategies learned during education while gaining firsthand experience in managerial decision-making supported by meticulous attention to detail.
Pursuing certifications like CFA or CPA
To become a financial manager, pursuing certifications like CFA or CPA can significantly enhance your credentials. Certified Public Accountant (CPA) certification is vital for roles that emphasize accounting and tax preparation.
It demonstrates expertise in auditing, business structure analysis, and compliance with taxation regulations, all crucial aspects of the financial manager's role. On the other hand, Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) certification emphasizes investment management skills, which are fundamental for making strategic investment decisions as a financial manager.
These certifications not just improve knowledge but also verify one’s expertise in specific areas critical to the role of a financial manager.
Challenges Faced by Financial Managers
Financial managers face the challenge of adapting to market fluctuations and balancing risk with profitability. These challenges require them to navigate complex regulations and make strategic decisions in a dynamic financial landscape.
Adapting to market fluctuations
Financial managers are entrusted with the task of adjusting to market fluctuations. They must stay updated on economic conditions and their impact on investments, budgets, and financial strategies.
When market conditions shift, financial managers need to swiftly assess the situation and adjust investment portfolios or budget allocations accordingly in order to maintain financial health.
In a world where market uncertainties are common, this adaptability is crucial for protecting assets and achieving long-term financial goals.
Financial managers also utilize risk management strategies to navigate through market fluctuations. By diversifying investments across different asset classes, they can mitigate the impact of market volatility.
Moreover, staying informed about industry trends and monitoring economic indicators enables them to anticipate changes in the marketplace proactively. This adaptability ensures that financial managers can make well-informed decisions even amidst unpredictable market shifts.
Balancing risk and profitability
Financial managers are tasked with the critical role of balancing risk and profitability. They have to carefully evaluate investment opportunities while taking into account potential uncertainties involved.
This involves using financial analysis and forecasting skills to identify the most effective investment strategies that offer high returns while minimizing potential downsides. In this domain, risk managers work closely with financial managers to execute strategies that effectively mitigate risks without compromising profitability.
It's a precise and forward-thinking endeavor.
This strategic equilibrium requires careful attention to detail in analyzing market trends, comprehending economic indicators, and assessing the impact of regulatory changes on investments.
A strong understanding of these factors enables financial managers to make informed decisions that result in optimal outcomes for their organizations' financial well-being.
Navigating complex regulations
Financial managers encounter the challenge of carefully navigating a complex network of regulations that oversee the financial industry. These regulations stem from various sources, including federal and state governments, as well as industry-specific regulators such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA).
Financial managers must ensure compliance with these regulations to avoid legal issues and maintain the confidence of investors and stakeholders. This involves staying updated on changing regulatory requirements, understanding their implications for their organization’s operations, and making necessary changes to policies and procedures in response.
Financial managers also deal with international regulatory standards, adding another layer of complexity. For example, they may need to work through tax treaties between different countries if their organization operates globally.
Ensuring adherence to these diverse regulations often requires careful attention to detail and an ability to interpret complex legal language within a constantly evolving landscape.
As a result, financial managers play a crucial role in safeguarding their organizations against potential financial risks arising from non-compliance.
By integrating effective strategies for understanding and adapting to complex regulations into day-to-day operations while focusing on maintaining compliance standards throughout all aspects of finance, financial managers can shield their organizations from negative consequences associated with failing to navigate effectively through this intricate terrain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, financial managers greatly contribute to the financial well-being and success of an organization. Their responsibilities include preparing and analyzing financial reports, creating budgets, monitoring cash flow, and providing guidance on investment choices.
Strong analytical, strategic planning, and communication skills are essential for success in this field. The role of a financial manager is ever-evolving and presents challenges, but it is also gratifying for individuals who thrive in the finance industry.
FAQs
1. What is the overall goal of a financial manager?
The main task of a financial manager is to manage investments, prepare financial statements and implement strategies that will increase the value and profitability of their organization.
2. Can you explain some job duties for government financial managers?
Government financial managers work on budgeting, spending and tax-related issues. They also prepare detailed reports to ensure public funds are used effectively.
3. How does the role of credit managers differ from insurance managers in finance?
Credit managers oversee an organization's credit business while insurance managers handle risk management tasks including setting up company-wide insurance policies.
4. Are detail-oriented skills important for a financial advisor or manager?
Yes, being detail-oriented helps greatly as they need to analyze complex financial data, make investment decisions and ensure compliance with laws.



